Total Quality Manage...
18957 | 6 Apr 2023
Nowadays, customers are more than just a number; they are the number one asset of any company. For a company to survive in the market in the long term, owners and managers must see the company through the eyes of its customers and focus on building long-term relationships with them. The best way to do this is to develop a sales funnel and define the customer's lifecycle and journey through the sales funnel. Getting a comprehensive view of the customer lifecycle and the customer's journey through the sales funnel is a challenging task based on a strategy that provides accurate insights into customer behavior with a mental focus on meeting customer needs and wants.
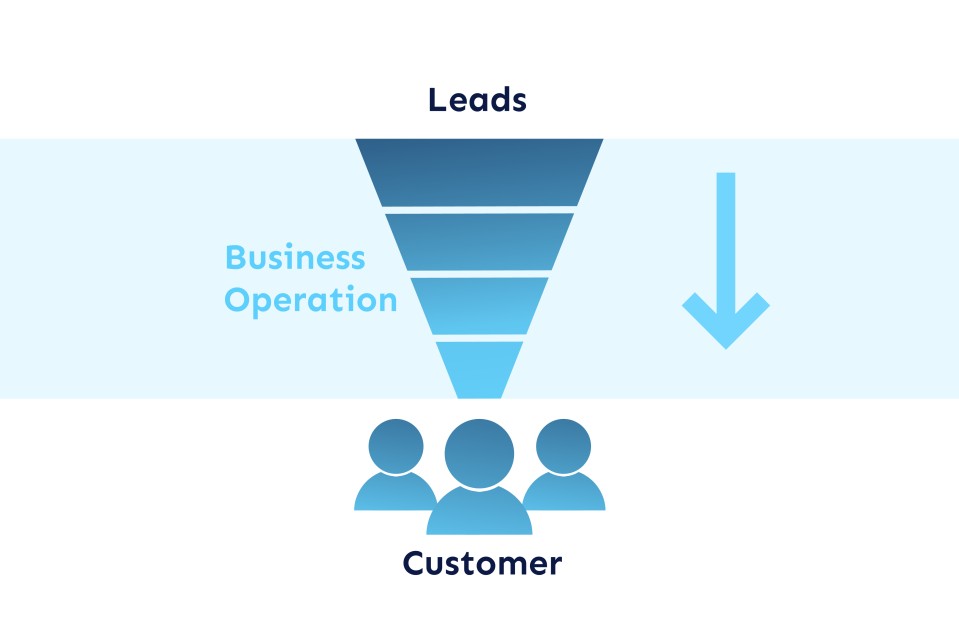
The Sales Funnel is a visualization tool represented by a framework designed to highlight the experience from a potential customer's first contact with a company to the sales and post-sales phases. It illustrates the stages a potential customer goes through before becoming a customer. The sales funnel, both in theory and in practice, appears under different names, such as the buyer's funnel, the sales cycle, the purchase process, etc. A sales funnel provides a way to create an exceptional experience across channels and devices to interact and engage with potential customers to convert them into actual customers and advocates who will attract new customers. The sales funnel is understood by marketers as the journey that the consumer takes from awareness to consideration and to the stage of deciding to purchase a product or service.
A sales funnel resembles a funnel or an inverted pyramid. It is widest at the top and narrowest at the bottom. With each stage of the funnel, the most qualified leads are promoted to the next stage. As a prospect moves through each stage of the sales funnel, they make a deeper commitment to purchase a product or service. You could say that the sales funnel is a kind of map the customer follows on their journey through the buying process. The stages of the sales funnel describe the steps through which the percentage of deviation from the potential to purchase leads is shown between the stages, forming a complete picture of the customer journey and highlighting areas for improvement since the sales funnel is directly related to the stages of the customer life cycle. Each stage within the sales funnel must be tailored to the business and nurtured in the context of customers, market paths and business goals. Each interaction between potential customers and the company is, thus, unique and different from the last.
Sales Funnel and Customer Journey are two terms that are closely related but not synonymous. A Customer Journey is a detailed description of the steps that turn a potential customer into a paying customer, while a Sales Funnel is a model that companies use to track potential customers through the various stages of the buying cycle. Also, Customer Journey and Customer Lifecycle are different terms, but they are similar in that they both define the movement of a customer through the sales funnel.
The sales funnel helps you understand what potential customers are thinking and doing at each stage of the buying process. These insights enable companies to invest in the right marketing activities and channels to deliver the most relevant messages at each stage. While it's nearly impossible to retain all leads that enter the sales funnel, it's crucial that companies make an effort to retain those who are ready to make a purchase. Determining the right stages within the sales funnel can be complex, so companies must have an appropriate Customer Relationship Management system in place.
The biggest problem in establishing the sales funnel stages is the excessive amount of customer information scattered across multiple marketing channels. Some CRM solutions automatically generate activity reports within the sales funnel and dynamically update conversion rates at each stage of the funnel over time, allowing companies to identify weaknesses within each stage of the sales funnel and make targeted improvements. In addition to defining and tracking KPIs and conversion rates at each stage, it is also imperative for companies to have a clear picture of the effectiveness of the sales funnel. Sales funnel performance reports play a key role in any sales strategy, helping to identify where companies should focus their marketing efforts in the future, and are a great help in predicting sales and seasonal trends.
The Traditional Sales Funnel (Figure 1) represents the old marketing mentality based on the rule of quantity over quality. American advertising and sales pioneer E. St. Elmo Lewis first proposed the AIDA model in 1898. The AIDA model was initially developed to define a person's cognitive stages when buying a product or service. It was a practical sales tool that incorporated then-current customer research in the marketplace to facilitate the management of personal selling mechanisms. E. St. Elmo Lewis believed that the most successful salespeople followed a four-step hierarchical process that utilized the four cognitive stages consumers go through when they adopt a new idea or purchase a new product or service. The sales funnel, according to the AIDA model, is, therefore, a way of procedurally attracting consumers from the awareness or consciousness stage, when a potential customer first learns about a company, to the purchase stage, when the potential customer is actually ready to buy a particular product or service.
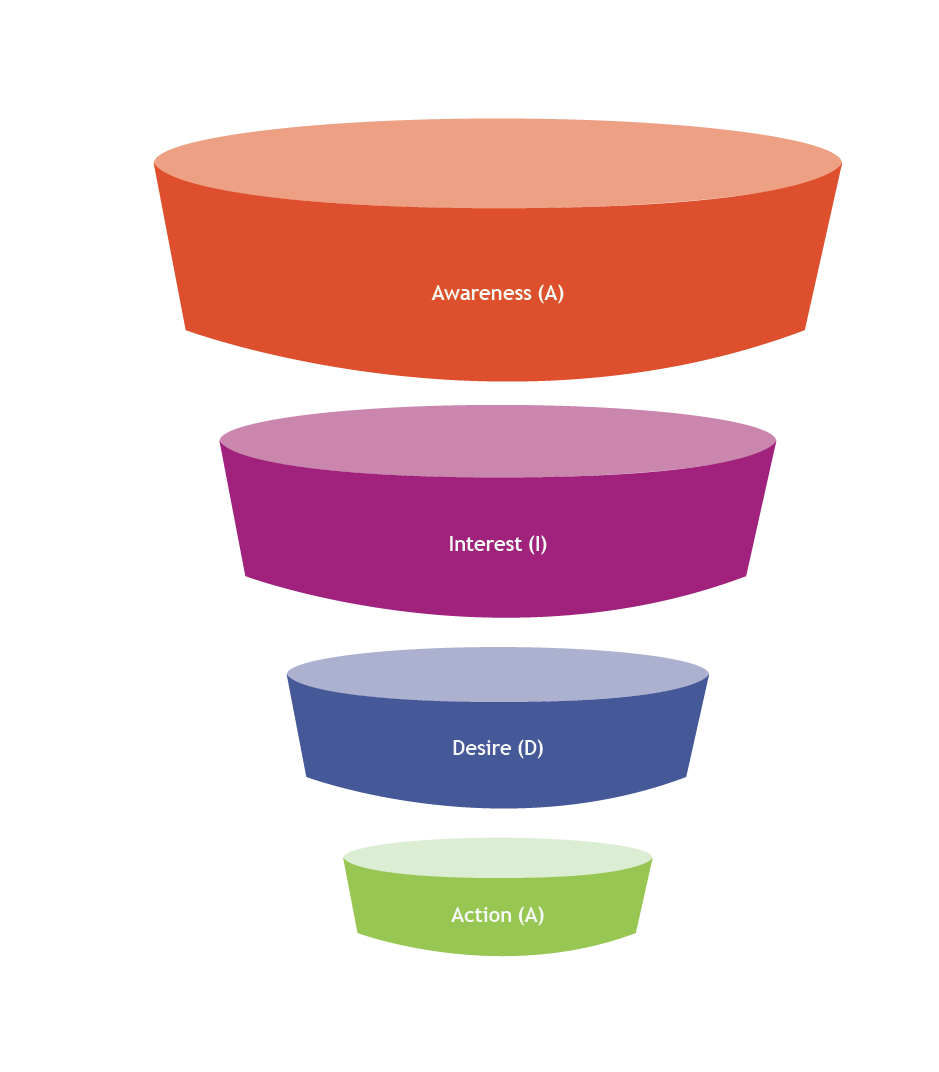
Figure 1: Sales Funnel according to the AIDA model
The AIDA model (Figure 1) represents an element of the purchasing process consisting of four phases:
Initially, the AIDA model was used to understand the sales process and train salespeople for B2B (Business To Business) and B2C (Business To Customer) sales. Long before digital marketing, the idea was to convince the customer through personal contact and bring them through the sales funnel. But little by little, marketers gradually began to think they should also include a customer perspective approach in the AIDA model. Therefore, the profession is increasingly moving away from the current model as opinions begin to form that the AIDA model is too mechanistically simplistic to be able to describe the sequence of nurturing phases through which customers move from awareness to purchase.
In the 1990s, the AIDA model was considered a revolutionary and proactive marketing formula for customer acquisition. The AIDA model is still helpful in describing a complex process and a good visual example to show the whole process from the beginning to the end of a customer's sales journey. It is one of the many models companies use to align their sales funnels. It describes the primary process by which people are motivated to buy and is based on the extrinsic incentives of salespeople. This motivation to buy depends on the AIDA model's four phases (described above). Both marketing teams and sales managers often apply strategies, tools, and techniques aimed at optimizing each phase of the sales process. Although traditional sales funnel models are still relevant, cyclical approaches that continue in a loop or hourglass shape are increasingly used instead of a linear funnel.
The mindset and structure of the traditional sales funnel are outdated in today's market context. Although modern sales funnels generally still summarize the basic steps of traditional models, today's models are much more complex. Today, a customer's experience with a company begins much earlier, before the individual even becomes a customer. People have incredible access to information thanks to television, the Internet and 24-hour news. For this reason, old sales funnels or models based on concepts that push people to buy a product or service are no longer the optimal solutions for long-term growth.
Companies, therefore, need to implement a modern multi-stage customer journey sales funnel. It is necessary to recognize that each step can be an opportunity for companies to engage with potential customers and provide them with a consistent and integrated experience that leads not only to purchase but also to an endorsement of the company. The ideal sales funnels are constantly changing in the new information age. Today's sales funnels are no longer linear like they used to be. Today, these contain a comprehensive view of the customer throughout the journey and are displayed in an hourglass shape, bringing together the synthesis of the sales funnel, the customer journey map and the customer life cycle. Namely, the customer journey does not end where the sales funnel ends but continues through further stages of the customer lifecycle.
Building a sales funnel is so important today. Most companies use an hourglass version as the basic model for building their sales funnel, within which they define the structure and frame of reference according to their needs. Modern sales funnel models incorporate digital marketing concepts and don't just consist of four steps, and they don't suddenly stop when customers make a purchase. They're designed to account for many complex customer experiences, from the very into the sales funnel to the post-purchase stages.
In the digital age, more precise and relevant funnels are used in marketing today, but the AIDA model provides a solid foundation for understanding the concepts of sales funnels. This is good news for companies that have kept up with changing sales and marketing trends but not so good for companies that have not recognized that the game has changed. For example, the modern sales funnel no longer has the classic conical shape but takes the form of an endless loop (Figure 2). It is a new and improved approach to designing the sales funnel to continuously deliver value and engagement at every stage of the relationship with a potential or actual customer. This approach enables real-time response to customer needs, which elevates customer relationships to a higher level. Post-sales processes are critical to further building relationships and fostering loyalty to the company. The modern sales funnel does not end once the customer makes a purchase. The modern sales funnel helps us understand what stages the customer goes through and informs us how we can improve the quality of the customer experience by providing a consistent and seamless experience across all touchpoints and across all channels.
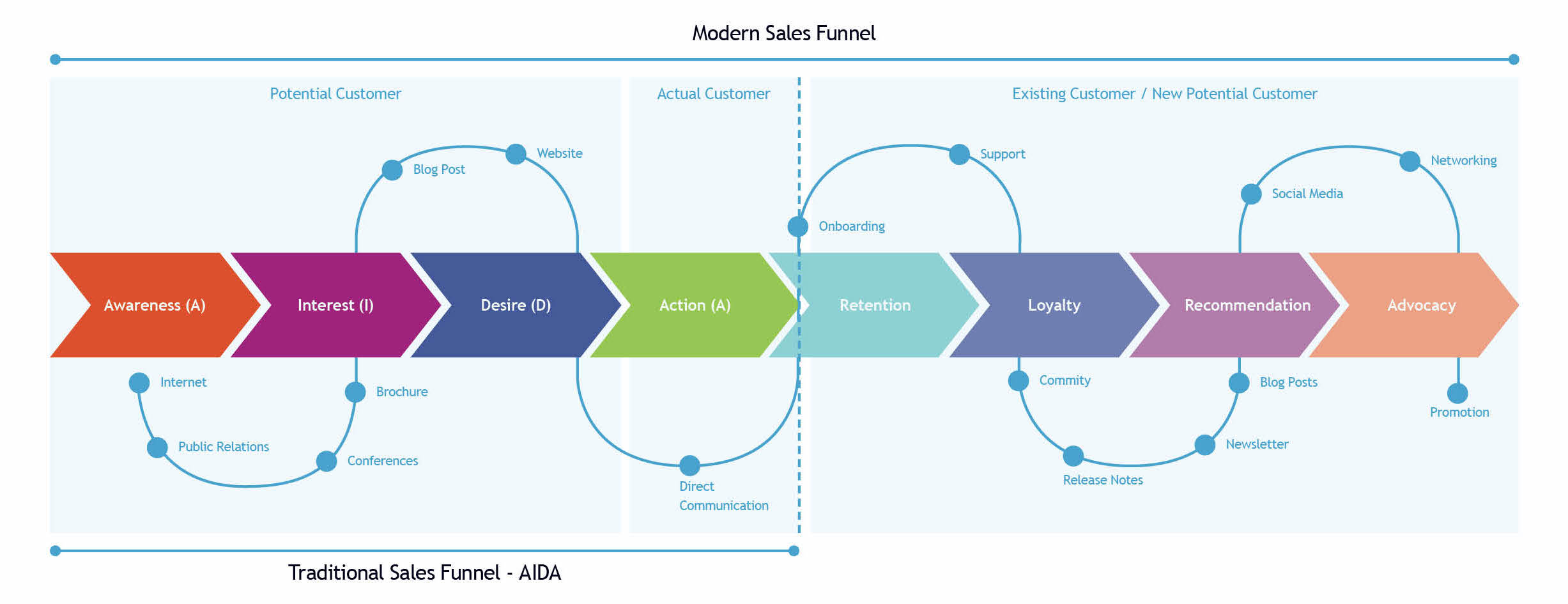
Figure 2: Modern Sales Funnel model
The Modern Sales Funnel initially contains four stages taken over from the traditional AIDA model. As it progresses, the modern sales funnel, unlike the traditional one, transitions into a retention side for marketing efforts, where customers are always treated as potential customers, even if they have already made a purchase. What happens in the mirror image of the funnel after the purchase phase symbolizes the second half of the never-ending customer journey. This modern approach helps provide continuous customer value at every sales funnel stage. Today, technology has advanced to the point where the method can be used really effectively. The information obtained about potential and existing customers can be used for tailored marketing with a high degree of personalization.
In conclusion, the Sales Funnel is an effective tool for businesses to visualize and understand a customer's journey through the buying process. It is important for businesses to focus on building long-term relationships with their customers and to see their company through the eyes of their customers. By using the Sales Funnel framework, businesses can create exceptional experiences for potential customers, engage and convert them into actual customers, and retain them by identifying weaknesses and making targeted improvements. The AIDA model is a traditional Sales Funnel that represents the cognitive phases that consumers go through when adopting a new idea or purchasing a new product or service. Overall, understanding the Sales Funnel and the customer journey is essential for businesses to make informed decisions about marketing activities, improve customer satisfaction, and increase sales. To properly implement and manage customer relations, companies must know the business system as a whole, which requires knowledge of Business Systems Engineering.
What are your thoughts on the subject above? Feel free to post a comment or start a discussion.
What are the implications of the awareness-to-purchase journey described by the AIDA model for digital marketing, especially in terms of content and engagement strategies? Visit us Telkom University
Leave A Comment