Total Quality Manage...
18560 | 6 Apr 2023
Business processes are the backbone of any successful organization. They offer a systematic way to execute daily operations, ensuring tasks are accomplished with precision, consistency, and compliance. By documenting and analyzing each process, organizations can uncover areas of improvement, cut costs, boost productivity, and shorten turnaround times. Business processes also help companies comply with legal and regulatory standards, steering clear of disputes and penalties. They enable organizations to stay nimble and adapt to changes in the business landscape while promoting open communication and teamwork among team members.
Business process modeling is a powerful practice that can transform the way organizations operate. By creating visual representations of their processes, companies can easily identify inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement to make necessary changes to boost productivity and customer satisfaction.
Through business process modeling, companies can gain a comprehensive understanding of their workflows, remove redundancies, and minimize errors, leading to cost savings and faster turnaround times. In addition, the practice helps identify opportunities for automation, allowing companies to streamline their operations and improve their customer experience.
Whether you use simple flowcharts or complex process maps, accuracy and clarity are key to successful process modeling. Once the diagrams are complete, they can be used to communicate the process to stakeholders, identify areas for improvement, and develop solutions to optimize operations.
Business process modeling aims to provide organizations with a comprehensive and detailed understanding of their operations. This enables the organization to establish consistency and gain control over its processes, identify and eliminate inefficiencies, and create a clear beginning and end for each process. By analyzing and modeling its processes, an organization can gain insight into how work is done, identify areas for improvement, and develop strategies to optimize its operations.
One of the key advantages of business process modeling is that it helps organizations to inventory their processes. This allows the organization to identify redundancies and streamline its workflows, leading to improved efficiency and productivity. Additionally, modeling enables organizations to combine similar processes and predict their performance, providing a better understanding of how different processes interact with each other.
Business process modeling is typically performed using specialized software tools that facilitate the creation of graphical representations of processes. These tools make it easy to create flowcharts, programs, hypertexts, scripts, and other visual representations of processes, making it easier for analysts and managers to understand and optimize the organization's workflows.
Ultimately, modeling business processes aims to enable organizations to achieve better results. By understanding how things work now and how they can be improved, organizations can develop strategies to optimize their operations and achieve their goals more efficiently. This can lead to cost savings, increased productivity, and improved customer satisfaction, making it an essential practice for any organization looking to improve its operations.
Business processes can be complex, which is why organizations have turned to visual representations to better understand and improve them. Initially, businesses used pen and paper to model their processes, but they have become digitized over time.
Business process modeling tools have made it possible to visually represent active processes within organizations and identify areas for improvement. These tools aim to accurately display all critical information necessary for the successful execution of a given process. They differ from each other in terms of functionality, performance, price, and user-friendliness. Some tools are purely graphical, while others enable holistic analysis and simulation to discover bottlenecks, shortcomings and potential business threats.
With the rise of information technology, there have been many advancements in business process modeling techniques and tools. There are several business process modeling techniques and tools available, each with its unique features. These tools should contain the following features: ease of use, modeling capabilities, analysis and simulation tools, report creation, and connectivity with other tools.
One of the most popular process modeling techniques and the tools associated with them are:
ARIS (Architecture of Integrated Information Systems) is a modern approach to modeling organizations that provide methods for analyzing processes and a holistic view of process planning, management, steering, workflow, and processing. ARIS is a concept that aims to express business processes in a precise way to enable detailed analysis and provide an unambiguous baseline for potential improvements.
At the core of ARIS is the EPC, which connects all other views and describes the dynamics of the business process. While the latest versions of the ARIS toolkit support BPMN for business process modeling, ARIS is not strictly a tool but a comprehensive approach to modeling organizations.
ARIS is an architecture for describing business processes and provides modeling methods with associated meta-models included in information models. It contains two dimensions that reduce the complexity of organizational processes, dividing them into views and levels. The ARIS Toolset software system provides modeling support, and the ARIS house represents a concept for comprehensive management of business processes at all levels of decision-making in the organization.
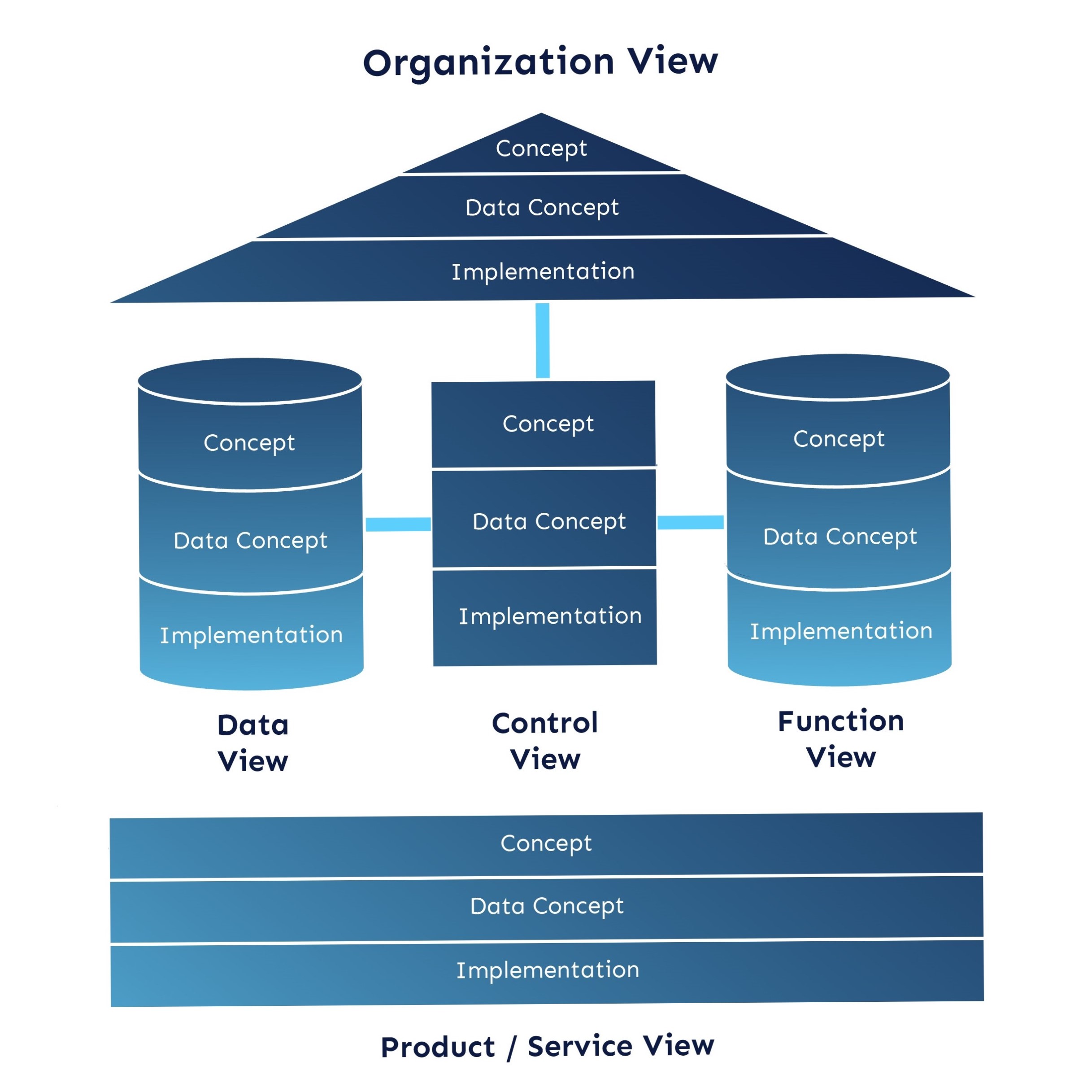
Figure 1: ARIS house concept (adapted from Scheer, 2004)
To use the ARIS tool effectively, it's essential to have a good understanding of its key concepts (Davis and Brabander, 2007):
The ARIS method involves implementing the ARIS concept in the ARIS platform using specialized products like ARIS Business Designer or ARIS Business Architect. ARIS diagrams are used to visually represent specific types of models that contain objects and connections stored in the underlying ARIS database. Each diagram is based on a well-defined notation and is part of a collection of related ARIS models that make up a business model. These models are organized into a database, which can be stored on servers located on a personal computer as an ARIS local area or on an ARIS network server. This allows for the business model to run in a single data collection or across multiple databases on different servers.
In conclusion, the use of process modeling in business is becoming increasingly important in today's fast-paced and ever-changing environment. It provides organizations with a better understanding of their processes and helps them identify areas for improvement, allowing them to streamline operations, reduce errors, and achieve better results. Careful attention to detail is critical when creating process diagrams, as even minor discrepancies can impact the overall functioning of the process. By implementing process modeling, businesses can gain a competitive advantage, improve customer satisfaction, and position themselves for long-term success.
What are your thoughts on the subject above? Feel free to post a comment or start a discussion.
Leave A Comment