Total Quality Manage...
18407 | 6 Apr 2023
Business processes are an essential aspect of any organization. Organizations undertake a series of steps or activities to achieve their objectives efficiently and effectively. A well-designed business process can help an organization achieve its goals, maximize productivity, and reduce operational costs. On the other hand, a poorly designed process can lead to inefficiencies, errors, and delays. Whether you are a business owner, manager, or employee, understanding business processes is essential for improving productivity, quality, and customer satisfaction.
A business process is a set of interconnected activities designed to produce an organization's specific output or outcome. These activities can be simple or complex, and they may involve people, technology, and other resources.
Business processes contain:
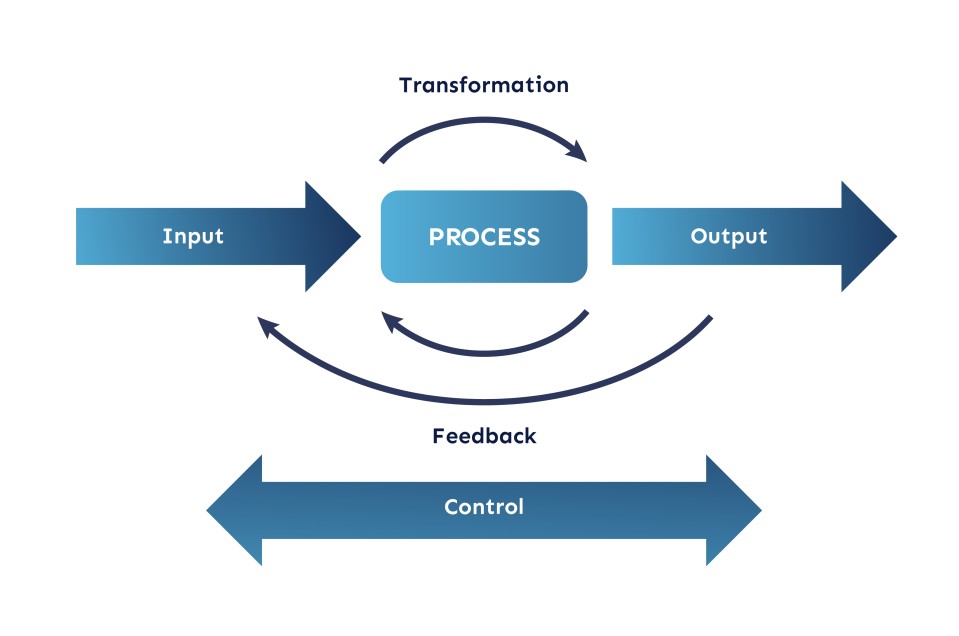
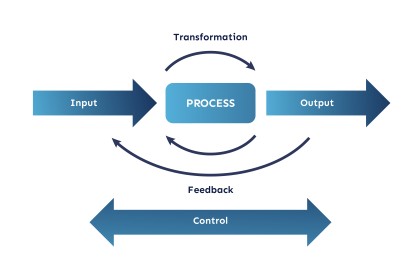
At the core of any business process is a sequence of steps that transform inputs into outputs. These steps are typically carried out in a specific order, with each step building on the previous one. The inputs to a process can be anything that is required to produce the desired output, such as raw materials, data, or information. On the other hand, the outputs of a process are the results or products of the process, such as a finished product, a report, or a service.
Business processes are overseen by process owners, who hold responsibility for the execution and control of the process. In each process, they must consider the limitations and costs of implementation, including necessary resources, in order to ensure efficient and successful execution. Additionally, time is crucial, with the necessary time units and key success factors defined by the process goals.
Business processes encompass all organizational activities, from production to administrative procedures. A more precise definition characterizes business processes as networks of connected activities with defined boundaries and priority relationships that utilize resources to transform inputs into outputs that meet the organization's needs. The goal of business process design is to determine optimal paths, and formally, this can be described as a process architecture configuration including inputs and outputs, flow units, a network of activities and buffers, resources, and information structure, with the aim of meeting performance requirements.
Process architecture comprises five main elements:
There are numerous reasons for modeling and listing business processes, including improving understanding of the process, creating a complete picture of the business for better control, detecting weaknesses in implementation, proposing renovations and testing them before implementation, and understanding the information needs of process operators.
Business processes can be classified into different categories based on their function within the organization. For example, there are production processes that are involved in creating a product or service, and administrative processes that are involved in managing the day-to-day operations of the organization. Other types of processes include sales, marketing, and customer service.
To illustrate the concept of a business process, let's take the example of a manufacturing process for a car. The inputs to this process may include raw materials such as metal, plastic, and glass, as well as data such as blueprints and engineering specifications. The process may involve multiple steps, such as stamping the metal into the desired shape, assembling the car's various components, and painting the finished product. The output of this process is a completed car that can be sold to customers.
In addition to the steps involved in a business process, other important elements must be considered. For example, there may be specific time constraints that must be adhered to, such as production schedules or delivery deadlines. Quality control measures may also be in place to ensure that the output of the process meets certain standards or specifications.
Furthermore, every business process has a process owner, who is responsible for overseeing the execution of the process and ensuring that it is carried out in a timely and efficient manner. The process owner may also be responsible for monitoring the performance of the process and making changes to improve its efficiency or effectiveness.
Every organization contains processes through which it carries out its business activities. These activities involve several stakeholders who must be familiar with the exact steps necessary to effectively realize the company's goals. The processes can be short and uncomplicated initially, with growth organizations becoming more complex. Risks arise that reduce the effectiveness of the organization's operations. These risks are most often shown in transport between departments, communication, repeating activities and performing unnecessary activities.
By modeling business systems, companies ensure the transparency of their processes and, based on these, determine their processes by performing analyses efficiently. The described processes are the basis for efficient and successful management of business processes and the organization as a whole.
In summary, a business process is a set of interconnected activities that are designed to produce a specific output or outcome for an organization. These activities may involve people, technology, and other resources, and they are typically carried out in a specific order. Understanding the concept of a business process is essential for improving productivity, quality, and customer satisfaction within an organization.
What are your thoughts on the subject above? Feel free to post a comment or start a discussion.
Leave A Comment