Total Quality Manage...
18411 | 6 Apr 2023

Quality is an important factor in any business, but what does it really mean? According to ISO (International Organization for Standardization), quality refers to the level to which a set of inherent characteristics meets specific requirements. To ensure that a business meets these requirements, it needs quality management. ISO defines quality management as coordinated activities that direct and control an organization with regard to quality. This means that a business needs to have a plan and process in place to ensure that it produces quality products or services. That's where QMS (Quality Management System) comes in.
QMS refers to the activities that businesses carry out to satisfy customer expectations related to quality. It includes an organizational structure, procedures, processes, and resources necessary for planning and implementing a product or service, with emphasis on areas that can affect an organization's ability to meet needs. But it doesn't stop there. QMS also refers to the activities that an organization carries out to control its processes with the aim of achieving the organization's objectives, which are to meet customer requirements and achieve compliance with regulations and laws. This means that QMS is about satisfying customers and ensuring that a business operates within the law and regulations.
So, what does a business need to do to establish QMS?
An organization must define its processes and how they interact, which resources are needed to produce the product or service, and how it will measure and improve the processes. Along with a quality manual and control, it must establish a system for managing documentation.
The ISO has outlined a set of elements that make up a Quality Management System (QMS). Let's take a closer look at each of these:
In short, an organization can achieve efficiency and success by systematizing and standardizing its way of working with a QMS. With each person knowing their roles and responsibilities and a standardized management system in place, organizations can be confident that they're following an international best practice model. And for organizations with complex processes, a QMS is essential for ensuring they're operating effectively.
Documentation is an important component of any Quality Management System (QMS) as it provides a systematic approach to managing and improving the quality of products and services. The documentation that can be applied through QMS includes a quality manual, which outlines the policies and procedures for the QMS and the quality policy, which describes the organization's commitment to quality. Additionally, the QMS should include quality objectives that define what the organization is trying to achieve in terms of quality.
Documented procedures and records are also required as part of the QMS. These procedures specify the steps that should be taken to ensure that products and services meet the desired quality standards, while records provide evidence that these steps have been taken. Examples of documented procedures and records may include quality control plans, inspection and test reports, calibration records, and corrective action reports.
Furthermore, the QMS documentation should include documents that the organization requires for its operations, such as work instructions, forms, and templates. Additionally, the documentation should include any legal or regulatory requirements that the organization must comply with, as well as any requirements from customers. Overall, having well-documented procedures and records as part of a QMS can help organizations ensure consistent and effective quality control and provide a basis for continuous improvement.
Quality Management principles are a set of fundamental beliefs and values that guide organizations to achieve their quality goals and objectives. These principles are the foundation of various international quality management standards, including ISO 9001, and they provide a framework for organizations to establish and maintain effective quality management systems.
There are eight Quality Management principles defined by ISO 9001:2015:
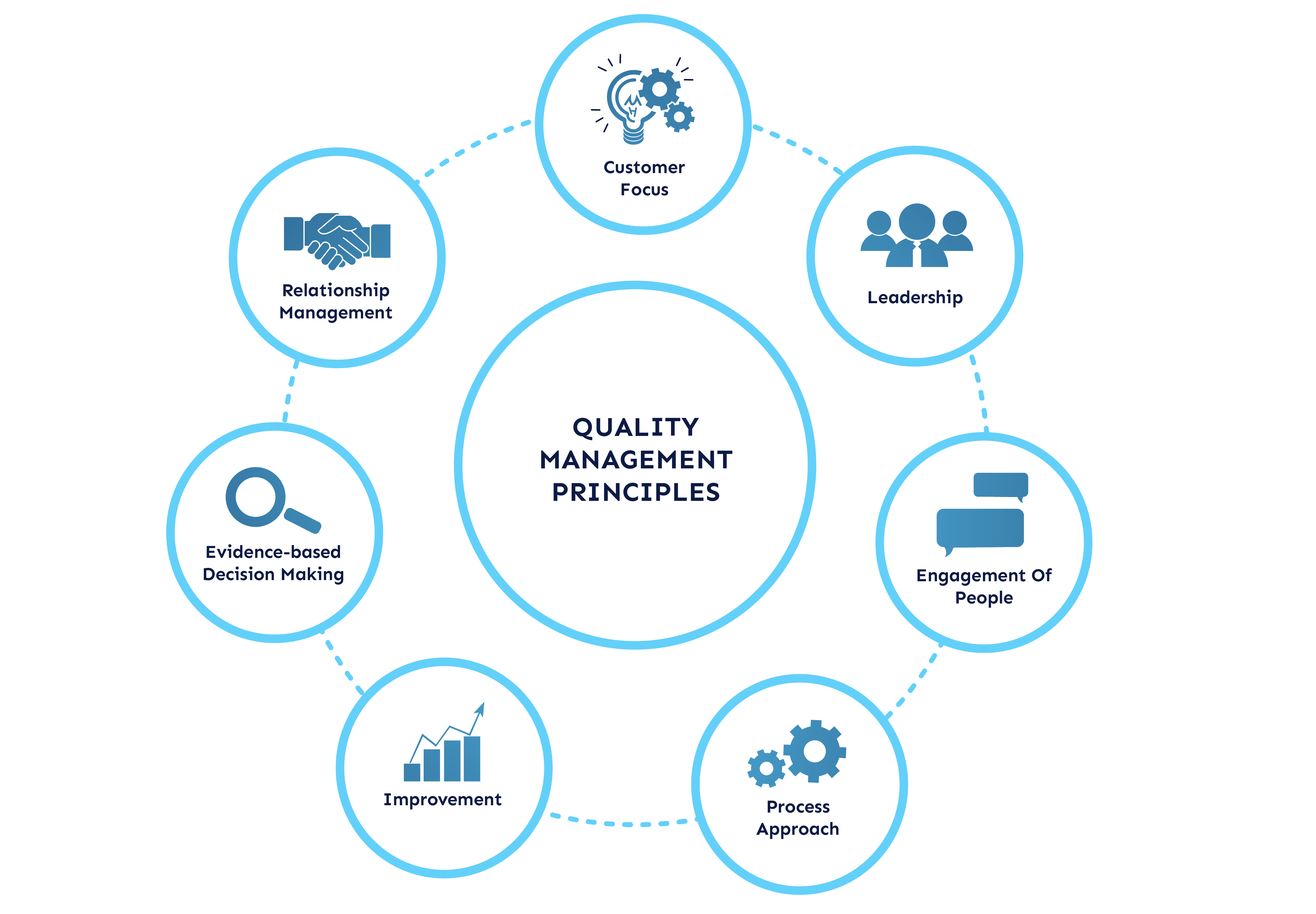
Figure 1: QM Principles
By applying these principles, organizations can achieve improved efficiency, enhanced customer satisfaction, and increased profitability. These principles can be adapted to any organization, regardless of size, sector, or industry.
Implementing a QMS requires a systematic and organized approach. An organization that adopts the approach mentioned above and executes all the stages gains trust in the capability of its processes and the quality of its products and establishes a foundation for continuous improvement. However, implementing a QMS must be planned carefully, with designated quality coordinators, disciplinary teams, quality teams, development of policies, gap analyses, process mapping, writing procedures, quality manuals, effective communication, training, audits, and accreditation. This approach ensures that the QMS is effectively implemented and continuously improved upon, meeting the organization's goals and expectations and satisfying the needs and expectations of interested parties.
Continuous improvement is an ongoing process, ensuring that the organization is continually looking for ways to improve and enhance its products and services while reducing waste and improving efficiency. Implementing a QMS involves several phases, starting with establishing the prerequisites for the ISO project.
The following are the key phases of implementing a QMS:
Overall, the successful implementation of a QMS requires commitment from top management, establishing a team responsible for implementing the QMS, promoting the importance of ISO, and providing necessary training. It also requires thorough planning, effective implementation, continuous internal auditing, and regular management reviews to ensure that the QMS works effectively and continually improves.
There are steps that need to be taken to achieve QMS Approach:
The following are the key phases of implementing a QMS:
In conclusion, the implementation of a Quality Management System (QMS) based on Total Quality Management (TQM) principles can be a game-changer for businesses. By following TQM principles and continuously improving through the use of data analysis and metrics, organizations can achieve greater efficiency, improved product and service quality, increased customer satisfaction, and a competitive advantage in the market. Don't settle for mediocrity - embrace the principles of TQM and establish a culture of continuous improvement to achieve long-term success!
What are your thoughts on the subject above? Feel free to post a comment or start a discussion.
I just finished reading your article on driving business excellence through quality management systems, and I must say, I'm thoroughly impressed. Your insights into the importance of a robust QMS are spot-on, and it's clear you've got a deep understanding of how it can truly elevate a company's performance.
Leave A Comment