Total Quality Manage...
18561 | 6 Apr 2023
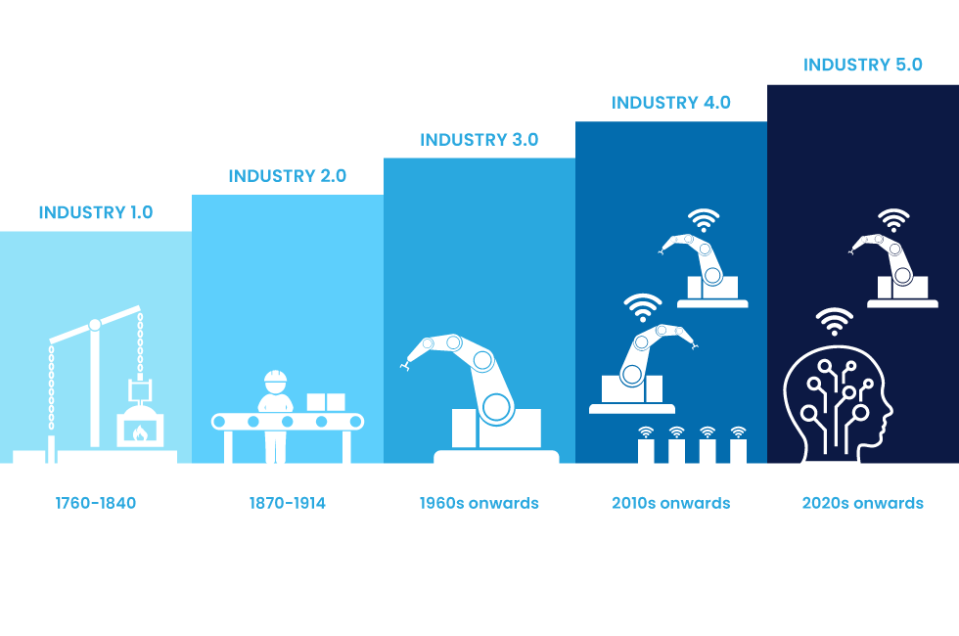
Throughout history, a series of major changes called industrial revolutions have completely transformed how we live, work, and engage with our surroundings. These revolutions, characterized by significant technological advancements and major shifts in how things are done, have had a lasting impact on society. They've not only changed the way our economies and industries function but have also fundamentally altered our day-to-day lives.
As we navigate the historical path paved by the First, Second, Third, and Fourth Industrial Revolutions, we find ourselves at the threshold of a fifth revolution. Industry 5.0 represents an exciting theoretical frontier where innovation meets sustainability, ethics, and unprecedented technological capabilities.
The evolution of industries represents a journey through time, reflecting our constant quest for progress. It all began with agrarian and craft-based economies, and then the First Industrial Revolution arrived with mechanization and steam power, bringing factories and urbanization. The Second Industrial Revolution, driven by electricity and assembly lines, gave rise to giants like the steel and automobile industries. In the late 20th century, the Third Industrial Revolution brought digital technology and automation, introducing computers, the internet, and global interconnectedness. The Fourth Industrial Revolution, Industry 4.0, is set to reshape industries through digital tech, automation, and data-driven decision-making, gradually transitioning into Industry 5.0.
The journey through these industrial revolutions began with the First Industrial Revolution, which marked the transition from agrarian and craft-based economies to industrialized ones. Key innovations included the steam engine, mechanized textile production, and the use of water and steam power in manufacturing. It began in the late 18th century and continued into the 19th century. During this era, the concept of mechanization and the harnessing of steam power laid the foundation for a shift towards large-scale manufacturing.
The First Industrial Revolution represented not only a technological transformation but also a profound societal shift. The world was brought closer together as steam engines powered factories, mechanized looms wove fabrics, and railroads connected distant regions. Urbanization saw the rise of industrial cities, and the division of labor became more pronounced. This revolution set the stage for a new economic order, as industries moved from cottage-based production to centralized factories. It was a time of both optimism and challenges, as newfound prosperity coexisted with labor struggles.
The story continues with the Second Industrial Revolution, a period characterized by significant advancements in manufacturing and technology. It saw the widespread adoption of electricity, the development of the internal combustion engine, and the introduction of assembly line production methods. This period of industrialization occurred from the late 19th century into the early 20th century. The electrification of industries and the mass production techniques introduced during this time significantly enhanced productivity.
The Second Industrial Revolution brought about a transformation in the way goods were produced and consumed. Electricity powered not only factories but also homes, leading to a rise in the standard of living. Innovations like the telephone and the automobile connected people and places as never before. The assembly line, pioneered by Henry Ford, revolutionized manufacturing, making products more affordable and accessible. This era also witnessed the emergence of the oil industry, which had a profound impact on energy and transportation.
Moving forward, we encounter the Third Industrial Revolution, often referred to as the Digital Revolution. This period was marked by the widespread adoption of digital technology, computers, and automation. Key developments included the emergence of microelectronics, the personal computer, the internet, and telecommunications advancements. The Third Industrial Revolution began in the mid-20th century and continued into the 21st century. It revolutionized the way information was processed and shared, connecting the world in ways previously unimaginable.
The Digital Revolution was not just about technological advancements but also a profound cultural shift. Personal computing empowered individuals, enabling them to access information and communicate globally. The internet emerged as a transformative force, reshaping industries like media, commerce, and entertainment. Automation and robotics began to redefine the workplace, changing how tasks were performed and demanding new skill sets. The rapid pace of innovation led to shorter product lifecycles, increased competition, and a need for adaptability.
The story doesn't end with the Third Industrial Revolution. We now find ourselves at the cusp of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, known as Industry 4.0. This era is propelled by the fusion of digital technologies, automation, artificial intelligence, and data-driven decision-making. In this age, factories become smart, supply chains more efficient, and machines imbued with an intelligence of their own. Industry 4.0 represents the ongoing transformation of manufacturing and industrial practices in the 21st century.
Industry 4.0 is not merely a technological upgrade; it's a fundamental reimagining of how industries operate. Cyber-physical systems and the Internet of Things (IoT) connect machines, products, and systems in real-time. Data becomes a strategic asset, enabling predictive maintenance and informed decision-making. Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms optimize processes and enhance productivity. Advanced robotics and additive manufacturing bring unprecedented flexibility to production lines. The workforce must adapt to a new era of human-machine collaboration, where creativity and problem-solving are valued alongside technical skills.
In Industry 4.0, several key technologies and concepts come to the forefront, reshaping industries and business models:
In theory, the concept of Industry 5.0, often referred to as the Fifth Industrial Revolution, represents a hypothetical stage of industrial development that would follow and build upon the foundation of Industry 4.0. This theoretical concept encompasses a range of advanced technologies and innovative approaches, potentially reshaping industries once again.
Theoretical discussions surrounding Industry 5.0 envision a future where the boundaries between physical and digital worlds blur even further. Quantum computing, with its ability to handle complex calculations at speeds unimaginable today, could unlock new frontiers in simulation and problem-solving. Advanced materials might redefine product design and manufacturing processes, enabling unprecedented levels of customization and sustainability. Biotechnology integration could lead to bio-inspired manufacturing processes and sustainable resource management, fundamentally changing how we produce and consume goods.
In a theoretical sense, Industry 5.0 could incorporate the following ideas and concepts:
Theoretical discussions surrounding Industry 5.0 raise important questions about ethics, governance, and societal implications. As technology continues to advance, it becomes increasingly crucial to ensure that innovations are harnessed for the benefit of all and that ethical standards are maintained.
It's important to note that the concept of Industry 5.0, if it were to emerge, would likely take shape gradually and depend on the evolving landscape of technology, industry needs, and societal expectations. The transition from one industrial revolution to the next typically unfolds over a significant period of time and involves various stakeholders, including governments, industries, researchers, and society at large.
In practice, the term "Industry 5.0" may or may not be adopted, and it is subject to evolving discussions and developments in the world of technology and industry.
The evolution of industry, from the First Industrial Revolution to the theoretical realms of Industry 5.0, is a testament to human ingenuity and our relentless pursuit of innovation. These industrial revolutions have reshaped economies, redefined industries, and transformed the way we live and work. As we stand on the precipice of Industry 4.0 and contemplate the possibilities of Industry 5.0, one thing remains clear: the journey of industrial transformation is far from over, and the future promises exciting new horizons in the world of technology and industry.
What are your thoughts on the subject above? Feel free to post a comment or start a discussion.
TAGS: Industrial Revolution, Industry 4.0, Industry 5.0, Technological Advancements, Manufacturing Transformation, Digitalization, Automation, Data-driven Decision-making, Technological Innovation, Economic Shifts, Societal Impact, Digital Technologies, Fourth Industrial Revolution, Fifth Industrial Revolution, Innovation and Progress, Smart Factories, Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), Advanced Robotics, Sustainability, Circular Economy, Quantum Computing, Biotechnology, Human-AI Collaboration, Advanced Materials, Ethical Considerations, Governance Frameworks, Urbanization, Labor Struggles, Historical Transformations.
Leave A Comment